Table of Contents
How Do The Kidneys Maintain Water Balance In The Body?
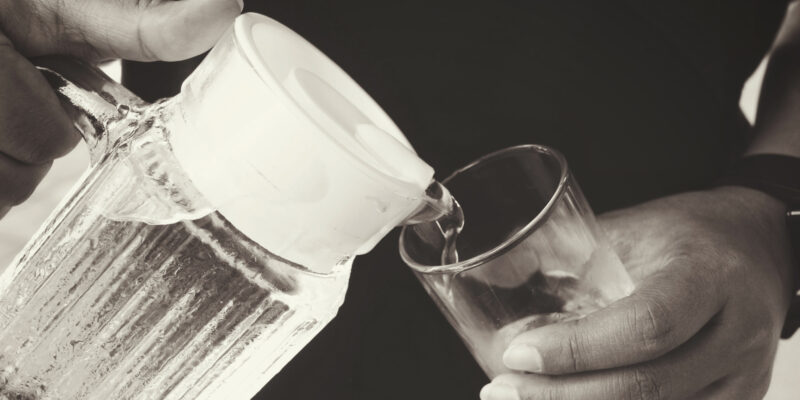
The kidneys perform two main functions: they filter waste products from our blood and they regulate the fluid balance of the body..
How does the kidney regulate water balance?
The kidney is the regulator of water balance. It does this by filtering out excess water and eliminating it through the urine. The process is called ‘osmosis’ which is the movement of water from a low water concentration area to high water concentration area. The kidney regulates the amount of water in the body by forming urine of the right concentration of water, minerals, and toxins..
How do the kidneys maintain water balance in the body quizlet?
The kidneys maintain water balance in the body by regulating the concentrations of urea and sodium in the blood. In this way, they maintain a constant internal environment in the body, which is necessary for the proper function of other organ systems. The kidneys help maintain homeostasis by excreting various substances from the blood in the form of urine..
Do kidneys keep water balanced in the body?
Kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood and removing unwanted substance from the body. The main function of the kidneys is to maintain the electrolyte balance of the blood by reabsorbing the salts which are transferred from the kidneys to the urine. The kidneys are responsible for producing ____% of the body’s total red blood cells. When the kidneys are working improperly, the ____% of the blood is lost with each cycle..
How do we maintain water balance in the body?
Of the total body weight, 60% is water. An adult loses between two and three pints of water every day in the form of sweat, urine, and respiration. If water intake is not sufficient to meet this requirement, the body will take water from the blood stream, which causes dehydration. Dehydration can lead to headaches, fatigue, and other physical problems. Disturbance of the body’s water balance can lead to serious health problems such as renal failure and heart failure. The kidney restores water and salts to the body by excreting urine. The blood stream and the cells of the body lose water and must be replenished. When water is taken into the body, it travels through the bloodstream and passes into the cells by osmosis, a process in which the water passes through the cell membranes and into the cells because it is attracted to the higher levels of solutes, such as salt, within the cells. Source: www.healthmasters.com/p/0/0/1/1/Water.html.
How do the kidneys function in maintaining homeostasis in fluid volume?
The kidneys play a major role in the maintenance of homeostasis in the body. The nephrons in the kidneys filter and remove waste products and excess water from the blood and eliminate waste and excess water in the form of urine. The kidneys not only maintain pressure, but also monitor the amount of water in the body and the amount of oxygen in the blood. If the body monitor finds that the body has too much water, then the kidneys will remove excess water in the form of urine. And when oxygen levels in the blood go too low, then the kidneys add more water to the blood. The kidneys also maintain plasma osmotic pressure in the body and control the body’s acid-base balance..
What are three ways the kidneys maintain homeostasis?
Kidneys are the organs that are responsible for filtering out the impurities from the blood and eliminating them through urination. The kidneys help maintain homeostasis in the body by balancing the amount of fluids and electrolytes in the body. Kidneys also balance the pH levels of the body. The three ways the kidneys maintain homeostasis are: The kidneys regulate the amount of fluids, electrolytes and acids in the body. They do so by releasing the correct amount of urine to maintain the balance, therefore, maintaining homeostasis. The kidneys control the pH level of the body by releasing hydrogen ions into the urine. If the kidneys fail, the pH level of the blood rises, which can cause death. The kidneys hold on to water molecules in the blood, thereby preventing dehydration..
How do kidneys work with other body systems to maintain homeostasis?
The kidneys are one of the most important organs in the human body, as they perform over 300 functions necessary for sustaining life. The kidneys are vital in the homeostasis of the body by balancing acidity, regulating blood pressure, excreting waste, regulating blood volume, filtering blood, producing hormones, maintaining electrolyte levels, regulating blood glucose levels, balancing levels of minerals, etc..
Which of the following are functions that the kidneys performs in maintaining homeostasis quizlet?
Renal Functions * Reabsorption of fluids * Excretion of wastes * Secretion of hormones * Maintenance of acid base balance (pH) * Formation of urine The kidneys perform many vital functions in the body. They make urine, which is composed of wastes and extra water. The kidneys filter the blood, removing wastes and excess water. The kidneys also make hormones that help make bone, control blood pressure, and make red blood cells. The kidneys also maintain the body’s acid-base (pH) balance. The kidneys also maintain the body’s acid-base (pH) balance..
Why do the kidneys need water?
The kidneys can function on a minimum of 1 glass of water per day, albeit less efficiently. The kidneys filter the blood, holding onto the minerals, vitamins, etc it needs to function, and dumping the rest into the urine. Without water, it cannot filter properly, and toxins build up in the blood stream..
How does homeostasis maintain water balance?
Homeostasis is the maintenance of internal equilibrium and is a fundamental characteristic of living systems. A living system will automatically maintain its normal physiological conditions through a complex and interconnected network of mechanisms. Homeostasis is essential for the survival of living systems. The body maintains homeostasis through five major control mechanisms that are responsible for the regulation of the following variables: ? Blood glucose level ? Blood volume ? Blood oxygen level ? Blood pH level ? Blood pressure.